Deploy Redis Stack using Bitnami’s Helm chart
Leverage the Bitnami Helm chart to deploy a Redis Stack server to a Kubernetes cluster.
Includes RediSearch, RedisJSON, RedisGraph, RedisTimeSeries, and RedisBloom
Background
A developer friend of mine reached out to me looking for a way to run Redis Stack server in Kubernetes, and he was already using the Bitnami Helm chart for Redis to deploy and run regular OSS Redis, so I decided to see if the Bitnami Helm chart would be flexible enough to use the Redis Stack server container image rather than the chart’s default Bitnami Redis image.
Long story short, you can, and thanks to flexible configuration options in the Bitnami Helm chart, everything can be deployed using a single helm command. This article will demonstrate how you can do this and explain how it works.
Disclaimer: I’ve only focused on getting this configuration to deploy successfully and verified the extended Redis features work by running some simple tests – I haven’t and wouldn’t run this in production without a lot more testing.
First, why Redis Stack?
Redis Stack is an extension of Redis that adds modern data models and processing engines to provide a complete developer experience.
In addition to all of the features of OSS Redis, Redis Stack supports:
- Queryable JSON documents RedisJSON
- Full-text search RediSearch
- Time series data (ingestion & querying) RedisTimeSeries
- Graph data models with the Cypher query language RedisGraph
- Probabilistic data structures RedisBloom
Deploy to Kubernetes using Helm
helm upgrade -i \
redis-stack-server redis \
--atomic \
--repo https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami \
--version 17.1.4 \
--values - <<EOF
global:
redis:
password: "weak"
image:
repository: "redis/redis-stack-server"
tag: "6.2.4-v2"
master:
args:
- -c
- /opt/bitnami/scripts/merged-start-scripts/start-master.sh
extraVolumes:
- name: merged-start-scripts
configMap:
name: bitnami-redis-stack-server-merged
defaultMode: 0755
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: merged-start-scripts
mountPath: /opt/bitnami/scripts/merged-start-scripts
replica:
args:
- -c
- /opt/bitnami/scripts/merged-start-scripts/start-replica.sh
extraVolumes:
- name: merged-start-scripts
configMap:
name: bitnami-redis-stack-server-merged
defaultMode: 0755
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: merged-start-scripts
mountPath: /opt/bitnami/scripts/merged-start-scripts
extraDeploy:
- apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: bitnami-redis-stack-server-merged
data:
start-master.sh: |
#!/usr/bin/dumb-init /bin/bash
### docker entrypoint script, for starting redis stack
BASEDIR=/opt/redis-stack
cd \${BASEDIR}
CMD=\${BASEDIR}/bin/redis-server
if [ -z "\${REDISEARCH_ARGS}" ]; then
REDISEARCH_ARGS="MAXSEARCHRESULTS 10000 MAXAGGREGATERESULTS 10000"
fi
if [ -z "\${REDISGRAPH_ARGS}" ]; then
REDISGRAPH_ARGS="MAX_QUEUED_QUERIES 25 TIMEOUT 1000 RESULTSET_SIZE 10000"
fi
[[ -f \$REDIS_PASSWORD_FILE ]] && export REDIS_PASSWORD="\$(< "\${REDIS_PASSWORD_FILE}")"
if [[ -f /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/master.conf ]];then
cp /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/master.conf /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/master.conf
fi
if [[ -f /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/redis.conf ]];then
cp /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/redis.conf /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/redis.conf
fi
\${CMD} \
--port "\${REDIS_PORT}" \
--requirepass "\${REDIS_PASSWORD}" \
--masterauth "\${REDIS_PASSWORD}" \
--include "/opt/bitnami/redis/etc/redis.conf" \
--include "/opt/bitnami/redis/etc/master.conf" \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redisearch.so \${REDISEARCH_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redisgraph.so \${REDISGRAPH_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redistimeseries.so \${REDISTIMESERIES_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/rejson.so \${REDISJSON_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redisbloom.so \${REDISBLOOM_ARGS}
start-replica.sh: |
#!/usr/bin/dumb-init /bin/bash
BASEDIR=/opt/redis-stack
cd \${BASEDIR}
CMD=\${BASEDIR}/bin/redis-server
get_port() {
hostname="\$1"
type="\$2"
port_var=\$(echo "\${hostname^^}_SERVICE_PORT_\$type" | sed "s/-/_/g")
port=\${!port_var}
if [ -z "\$port" ]; then
case \$type in
"SENTINEL")
echo 26379
;;
"REDIS")
echo 6379
;;
esac
else
echo \$port
fi
}
get_full_hostname() {
hostname="\$1"
echo "\${hostname}.\${HEADLESS_SERVICE}"
}
REDISPORT=\$(get_port "\$HOSTNAME" "REDIS")
[[ -f \$REDIS_PASSWORD_FILE ]] && export REDIS_PASSWORD="\$(< "\${REDIS_PASSWORD_FILE}")"
[[ -f \$REDIS_MASTER_PASSWORD_FILE ]] && export REDIS_MASTER_PASSWORD="\$(< "\${REDIS_MASTER_PASSWORD_FILE}")"
if [[ -f /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/replica.conf ]];then
cp /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/replica.conf /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/replica.conf
fi
if [[ -f /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/redis.conf ]];then
cp /opt/bitnami/redis/mounted-etc/redis.conf /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/redis.conf
fi
echo "" >> /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/replica.conf
echo "replica-announce-port \$REDISPORT" >> /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/replica.conf
echo "replica-announce-ip \$(get_full_hostname "\$HOSTNAME")" >> /opt/bitnami/redis/etc/replica.conf
\${CMD} \
--port "\${REDIS_PORT}" \
--requirepass "\${REDIS_PASSWORD}" \
--masterauth "\${REDIS_PASSWORD}" \
--include "/opt/bitnami/redis/etc/redis.conf" \
--include "/opt/bitnami/redis/etc/replica.conf" \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redisearch.so \${REDISEARCH_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redisgraph.so \${REDISGRAPH_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redistimeseries.so \${REDISTIMESERIES_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/rejson.so \${REDISJSON_ARGS} \
--loadmodule /opt/redis-stack/lib/redisbloom.so \${REDISBLOOM_ARGS}
EOF
Let’s breakdown what the above helm command is doing:
helm upgrade -iis shorthand to do ahelm installif a release doesn’t already exist, andhelm upgradeif one does.redis-stack-serveris the name of the helm release.redisis the name of the chart we want from the repo.--repo https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnamiis the endpoint for the webserver Bitnami uses to host their charts.--atomicwill implicitly wait for the entire release to complete and rollback if any component fails--version 17.1.4is Bitnami’s latest redis chart version at the time of this writing.--values -allows using a heredoc to specify the values to pass to the helm chart inline.global.redis.password: "weak"sets a password for all Redis nodes (master and replicas). Note: This is hard coded for demonstration only, not acceptable in most scenarios.image.repositoryandimage.tagallows us to use a custom image, in this case, we want to use the redis-stack-server image and the latest tag at the time of writing from Docker Hub.master.argsandreplica.argsare needed to execute custom bash startup scripts (more on that below).master.extraVolumes,replica.extraVolumes,master.extraVolumeMounts, andreplica.extraVolumeMountsneeded to mount the custom ConfigMap below as executable script files for above.extraDeployis a way to have this helm chart create a custom ConfigMap namedbitnami-redis-stack-server-mergedused by the above extra volumes/mounts. The ConfigMap combines the baked-in entrypoint.sh from the redis-stack-server container image and the startup scripts from the Bitnami helm chart for both the master and replicas. Requiring this “merge” of entrypoint/startup scripts in order to keep what’s needed from each won’t maintain well over time and is error-prone, hopefully, there is a better way.
Review what we deployed
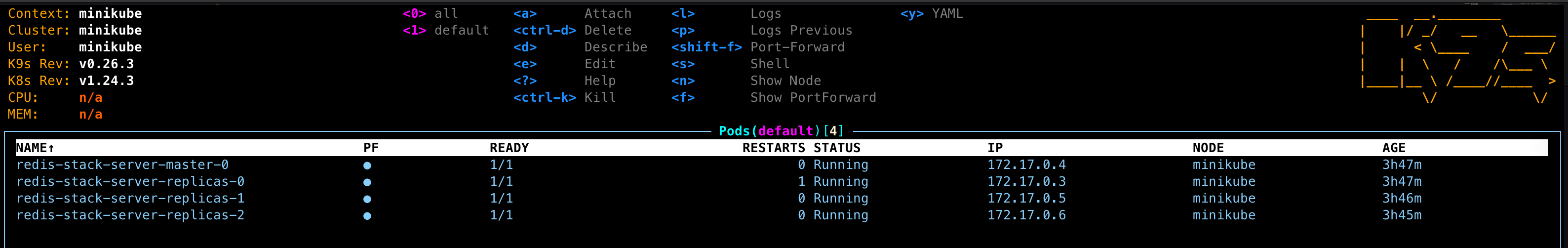
You should now have a single master (read/write) Pod and three replica (read-only) Pods, and associated Services in your Kubernetes cluster:
We can create a port forward to the redis-stack-server-master Service:
$ kubectl port-forward -n default svc/redis-stack-server-master 6379:6379
Then connect using any client tool for Redis – I’ll use one called Medis.
Connection info:
- Host: localhost
- Port: 6379
- Password: weak
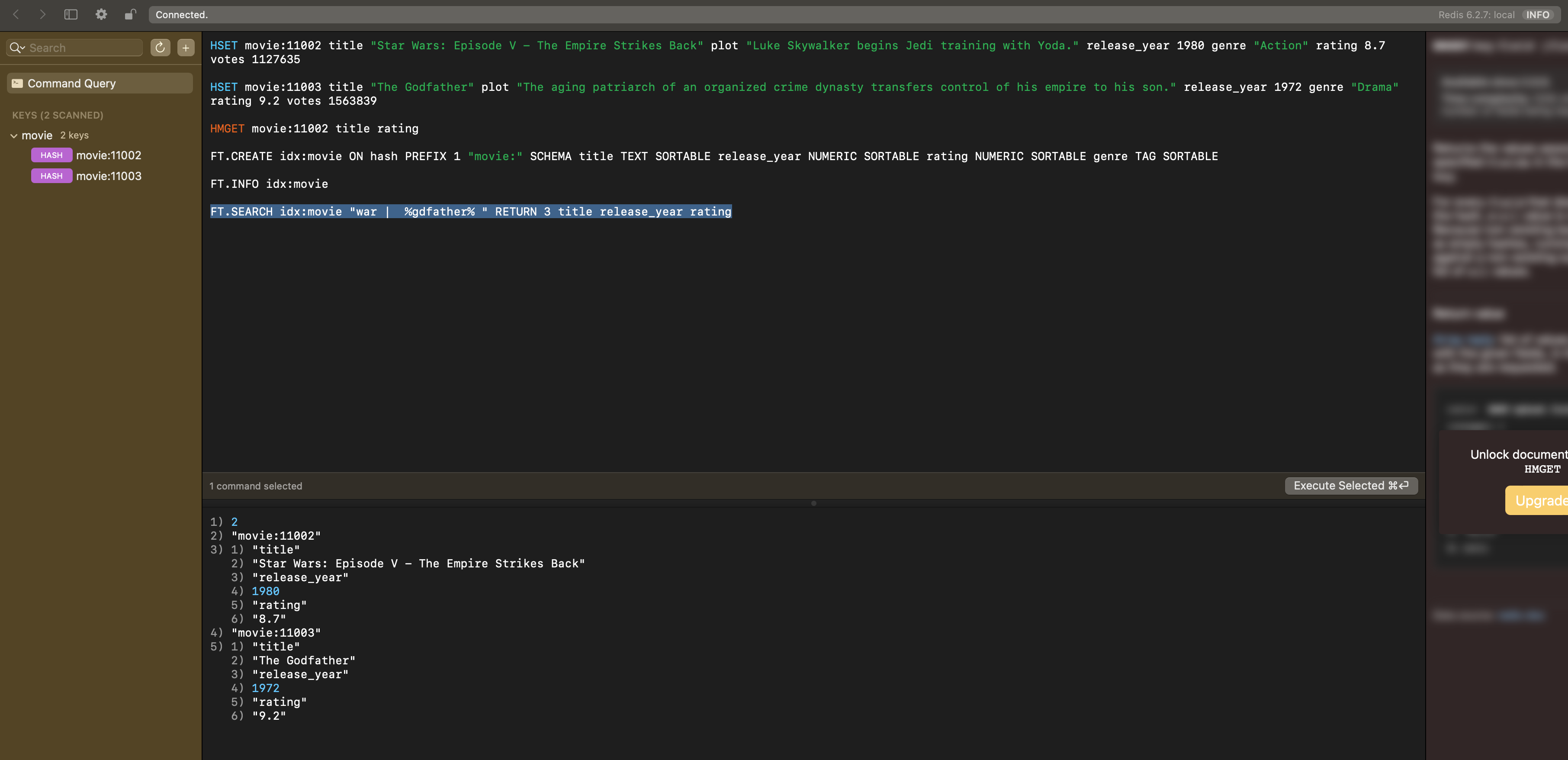
Now we can run the first three commands shown below that OSS Redis would be capable of running to ensure the basics are working, and then the last three commands that use the extended full-text search capabilities added by the RedisSearch module:
Conclusion
The Bitnami Helm chart for Redis has a lot of other configuration options that we didn’t cover in this article that could be used to create a more reliable production-grade deployment of Redis Stack – this article demonstrates how you could get started if you want to proceed down this path.
If you enjoyed this post I’d appreciate some claps for it over on Medium where you can follow me for more of the same.